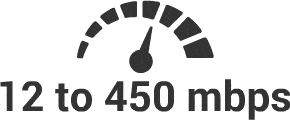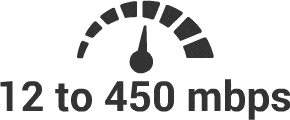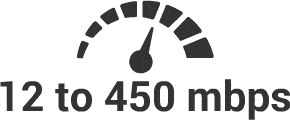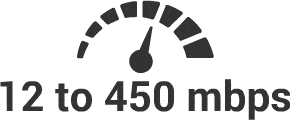
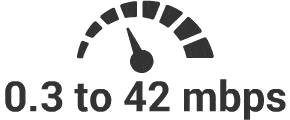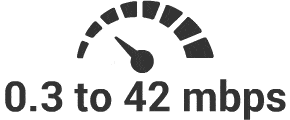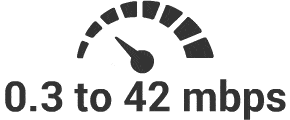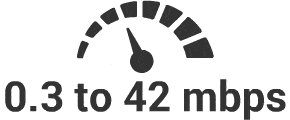
2030
Shorter Wavelengths will mean centimeter level
accuracy
(e.g., workers will be able to locate and examine any object on the
planet at data transfer rates up to 100x faster than 5G).

Digital Twins will facilitate remote training and maintenance
(e.g., virtually replicating physical entities such as people, devices, systems, and
even places)

Intelligent Machines will interface with other intelligent
machines
(e.g., machine vision will far surpass human capabilities, resulting in faster
diagnosis and remediation of complex problems)

Fully Immersive XR will become commonplace
(e.g., ambient
interfaces for maintenance and guidance in areas such as healthcare, education and
manufacturing).